Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Applied) single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensor
single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensorShishido, Hiroaki*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(4), p.1108 - 1113, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kimura, Yoshiki; Tsuchiya, Kenichi*
Radioisotopes, 72(2), p.121 - 139, 2023/07
Rapid and precise radioisotope identification in the scene of nuclear detection and nuclear security incidents is one of the challenging issues for the prompt response on the detection alarm or the incidents. A radioisotope identification algorithm using a deep artificial neural network model applicable to handheld gamma-ray detectors has been proposed in the present paper. The proposed algorithm automatically identifies gamma-emitting radioisotopes based on the count contribution ratio (CCR) from each of them estimated by the deep artificial neural network model trained by simulated gamma-ray spectra. The automated radioisotope identification algorithm can support first responders of nuclear detection and nuclear security incidents without sufficient experience and knowledge in radiation measurement. The authors tested the performance of the proposed algorithm using two different types of deep artificial neural network models in application to handheld detectors having high or low energy resolution. The proposed algorithm showed high performance in identifying artificial radioisotopes for actually measured gamma-ray spectra. It was also confirmed that the algorithm is applicable to identifying  U and automated uranium categorization by analyzing estimated CCRs by the deep artificial neural network models. The authors also com-pared the performance of the proposed algorithm with a conventional radioisotope identification method and discussed promising ways to improve the performance of the algorithm using the deep artificial neural network.
U and automated uranium categorization by analyzing estimated CCRs by the deep artificial neural network models. The authors also com-pared the performance of the proposed algorithm with a conventional radioisotope identification method and discussed promising ways to improve the performance of the algorithm using the deep artificial neural network.
Kozawa, Takayuki; Suganuma, Takuro; Homma, Fumitaka; Higashimura, Keisuke*; Ukai, Takayuki*; Saito, Kenji
JAEA-Technology 2023-007, 24 Pages, 2023/06
To improve the reliability of the HTTR wide range monitor in a high-temperature environment, structural changes of the wide range monitor were investigated. It was clear that the structure for directly joins of the MI cable core wire and metal tube instead of the joins with lead wire is the most reliable method with shortest way. From a result of the thermal cycle tests and high temperature endurance tests for a mock-up connecting this connection parts, it was clear that the soundness of the connection part was maintained under the usage conditions of the HTTR.
Kitayama, Yoshiharu
Gamma Ray Imaging; Technology and Applications, p.165 - 179, 2023/00
A gamma-ray imager is a powerful tool for visualizing the distribution of radioactive materials. Recently, it has been applied to the decommissioning site of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. At the decommissioning site, an imager compact, lightweight, and capable of quantitative evaluation of radioactivity is demanded. The Gamma-ray Imager using Small-Angle Scattering (GISAS) was proposed as a gamma-ray imager that meets all these requirements. GISAS consists of several shield-free directional gamma-ray detectors that detect only small-angle Compton scattering. Simulations and experiments verified the feasibility of the shield-free directional gamma-ray detectors. The shield-free directional gamma-ray detector consists of a scatterer that detects small-angle Compton scattering and an absorber that detects the scattered gamma rays. By setting an appropriate energy window for each detector, only scattering events that can be considered almost straightforward are detected. Through simulations and experiments, we have confirmed that using a silicon drift detector as the scatterer and a Gd3Al2Ga3O12 scintillator as the absorber, we can detect only small-angle Compton scattering events and obtain directionality for 662 keV gamma rays.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Koizumi, Tomokatsu; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Ebine, Masumi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room Temperature Semiconductor Detector Conference (2022 IEEE NSS MIC RTSD) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/11
A new thin position-sensitive scintillation neutron detectors have been developed to replace present scintillation detectors in SENJU diffractometer at J-PARC MLF. The SENJU diffractometer originally composed of 37 position-sensitive detectors, where each detector has neutron sensitive area of 256  256 mm with a pixel size of 4
256 mm with a pixel size of 4  4 mm. To renew some original detectors the new detectors have been developed based on ZnS scintillator and wavelength-shifting fibers technology. The developed replacement detectors were designed with a thin thickness of 12 cm, which is 40% of the original detector. The new detectors have also improved detector performances to the original ones in terms of detection efficiency (
4 mm. To renew some original detectors the new detectors have been developed based on ZnS scintillator and wavelength-shifting fibers technology. The developed replacement detectors were designed with a thin thickness of 12 cm, which is 40% of the original detector. The new detectors have also improved detector performances to the original ones in terms of detection efficiency ( 60% for 2-A neutrons) and count uniformity (5-8%). The produced six detector modules have been implemented to the beamline after checking their detector performances in the lab.
60% for 2-A neutrons) and count uniformity (5-8%). The produced six detector modules have been implemented to the beamline after checking their detector performances in the lab.
 Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response function
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response functionSato, Shunsuke*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Kashima, Takao*; Futakami, Kazuhiro*; Suyama, Kenya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.615 - 623, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new non-destructive method for evaluating  Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.  Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which
Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which  Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of
Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.
Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.  Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified
Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified  Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
Fukaya, Yuji; Okita, Shoichiro; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 168, p.108911_1 - 108911_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A power distribution monitoring system by using a moving detector for a core with a long neutron flight path has been proposed. High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) and Fast Reactor (FR) has a long neutron flight path and the neutrons reach to detector far from fuel assembly in the center of the core unlike Light Water Reactor (LWR). By using the feature, power distribution can be observed with a few detectors by moving the detector and computed tomography technology similar to X-ray Computed Tomography (CT). For a small-sized core, the power distribution can be evaluated only by an ex-core neutron detector. For a large-sized core with inner detectors, the power distribution can be observed with a small number of in-core detectors even if the deployment is limited due to material integrity conditions such as temperature environment. The feasibility is numerically confirmed by simulations of the HTGR core and its detector response. It is expected to observe the power distribution in the core of HTGR and FR, which is difficult continuously to deploy in-core detectors because of high temperature and/or high irradiation damage.
Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Seki, Misaki; Shibata, Akira; Nakamura, Jinichi; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-018, 42 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing various reactor materials, irradiation techniques and instruments for more than 30 years. Among them, the development of self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs) and gamma detectors (SPGDs) has been carried out, and several research results have been reported. However, most of the results are based on the design study of the detector development and the results of in-core irradiation tests and gamma irradiation tests using Cobalt-60. In this report, a numerical code is developed based on the paper "Neutron and Gamma-Ray Effects on Self-Powered In-Core Radiation Detectors" written by H.D. Warren and N.H. Shah in 1974, in order to theoretically evaluate the self-powered radiation detectors.
Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(9), p.2400505_1 - 2400505_5, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In this study, we employed a superconducting detector, current-biased kinetic-inductance detector (CB-KID) for neutron imaging using a pulsed neutron source. We employed the delay-line method, and high spatial resolution imaging with only four reading channels was achieved. We also performed wavelength-resolved neutron imaging by the time-of-flight method. We obtained the neutron transmission images of a Gd-Al alloy sample, inside which single crystals of GdAl were grown, using the delay-line CB-KID. Single crystals were well imaged, in both shapes and distributions, throughout the Al-Gd alloy. We identified Gd nuclei via neutron transmissions that exhibited characteristic suppression above the neutron wavelength of 0.03 nm. In addition, the
were grown, using the delay-line CB-KID. Single crystals were well imaged, in both shapes and distributions, throughout the Al-Gd alloy. We identified Gd nuclei via neutron transmissions that exhibited characteristic suppression above the neutron wavelength of 0.03 nm. In addition, the 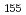 Gd resonance dip, a dip structure of the transmission caused by the nuclear reaction between an isotope and neutrons, was observed even when the number of events was summed over a limited area of 15
Gd resonance dip, a dip structure of the transmission caused by the nuclear reaction between an isotope and neutrons, was observed even when the number of events was summed over a limited area of 15  m
m  12
12  m. Gd selective imaging was performed using the resonance dip of
m. Gd selective imaging was performed using the resonance dip of 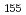 Gd, and it showed clear Gd distribution even with a limited neutron wavelength range of 1 pm.
Gd, and it showed clear Gd distribution even with a limited neutron wavelength range of 1 pm.
Mochimaru, Takanori*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takahashi, Tone; Hironaka, Kota; Kimura, Yoshiki; Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta; Yamanishi, Hirokuni*; Wakabayashi, Genichiro*
Dai-42-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/11
no abstracts in English
Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 7(4), p.042006_1 - 042006_7, 2021/10
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Koizumi, Tomokatsu; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Ebine, Masumi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2020), Vol.1, p.483 - 484, 2021/09
Two-dimensional neutron detectors were developed for the extension of SENJU time-of-flight Laue single crystal neutron diffractometer in J-PARC MLF. The detectors are to be installed at the additional detector bank for the SENJU instrument. The detector module is made based on ZnS scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technology, where each detector module maintains a neutron-sensitive area of 256 256 mm with a pixel size of 4
256 mm with a pixel size of 4 4 mm. To meet the tight space limitation in the instrument, the detector was designed as compact as possible. The detector has a depth of 170 mm, which is about 40% smaller than that of the original SENJU detector. All four produced detectors exhibited similar detector performances: detection efficiency 50-60% for 2-
4 mm. To meet the tight space limitation in the instrument, the detector was designed as compact as possible. The detector has a depth of 170 mm, which is about 40% smaller than that of the original SENJU detector. All four produced detectors exhibited similar detector performances: detection efficiency 50-60% for 2- neutron,
neutron,  Co gamma-ray sensitivity 1
Co gamma-ray sensitivity 1 10
10 , count uniformity 3-6%.
, count uniformity 3-6%.
Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1590, p.012033_1 - 012033_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Morishita, Yuki; Ye, Y.*; Mata, L.*; Pozzi, S. A.*; Kearfott, K. J.*
Radiation Measurements, 137, p.106428_1 - 106428_7, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have developed a compact, organic-scintillator-based alpha/beta spectrometer for radon measurements and have characterized it using a unique, small radon chamber. The spectrometer is composed of a through-silicon via (TSV) silicon photomultiplier (or SiPM) and a 6 mm  6 mm
6 mm  6 mm stilbene crystal cube. Analog signals from the SiPM are sent to a digitizer. The detector is housed in a light-tight box, with a stacked air filter installed in one side of the box to enable
6 mm stilbene crystal cube. Analog signals from the SiPM are sent to a digitizer. The detector is housed in a light-tight box, with a stacked air filter installed in one side of the box to enable  Rn gas to diffuse to the inside. We conducted one experiment with the spectrometer and an AlphaGUARD detector placed in a basement at the University of Michigan, and we conducted other experiments with both detectors placed in a small radon chamber together with
Rn gas to diffuse to the inside. We conducted one experiment with the spectrometer and an AlphaGUARD detector placed in a basement at the University of Michigan, and we conducted other experiments with both detectors placed in a small radon chamber together with  Ra sources. By applying a pulse-shape-discrimination technique, we were able to separate the alpha and beta spectra simultaneously and clearly and to measure them quantitatively. We found two peaks in the measured alpha spectrum: a lower-energy peak due to
Ra sources. By applying a pulse-shape-discrimination technique, we were able to separate the alpha and beta spectra simultaneously and clearly and to measure them quantitatively. We found two peaks in the measured alpha spectrum: a lower-energy peak due to 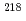 Po and a higher-energy peak due to
Po and a higher-energy peak due to  Po. We found a linear relation between the radon concentration y from AlphaGUARD and the counting rates from the stilbene-SiPM detector. The alpha/beta spectrometer is less than 10 mm thick, and we expect that it will be easy to increase the sensitivity with future device construction. Thus, this compact, organic-scintillator-based alpha/beta spectrometer shows promise for use in novel radon-detection systems.
Po. We found a linear relation between the radon concentration y from AlphaGUARD and the counting rates from the stilbene-SiPM detector. The alpha/beta spectrometer is less than 10 mm thick, and we expect that it will be easy to increase the sensitivity with future device construction. Thus, this compact, organic-scintillator-based alpha/beta spectrometer shows promise for use in novel radon-detection systems.
Iizawa, Yuki*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; et al.
Superconductor Science and Technology, 32(12), p.125009_1 - 125009_8, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:59.07(Physics, Applied)Nakamura, Tatsuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; To, Kentaro; Tsutsui, Noriaki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2018) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2019/10
A two-dimensional scintillation neutron detector with a submillimeter spatial resolution was developed for pulsed neutron diffraction imaging at the J-PARC MLF. The detector comprised the thin, single ZnS/ LiF scintillator screen coupled with the crossed wavelength-shifting fiber array for light collection. For a high spatial resolution, the wavelength shifting fibers with diameter of 0.1 mm were used them for assembling the detector. The prototype detector that has a neutron-sensitive area of 24
LiF scintillator screen coupled with the crossed wavelength-shifting fiber array for light collection. For a high spatial resolution, the wavelength shifting fibers with diameter of 0.1 mm were used them for assembling the detector. The prototype detector that has a neutron-sensitive area of 24  24 mm
24 mm exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.20
exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.20 0.06 mm and 0.16
0.06 mm and 0.16 0.06 mm for x and y directions, respectively. The detector had a detection efficiency of 7
0.06 mm for x and y directions, respectively. The detector had a detection efficiency of 7 for thermal neutrons with a
for thermal neutrons with a  Co
Co  -ray sensitivity in the order of 10
-ray sensitivity in the order of 10 . In this paper detailed detector design is presented together with experimental results using the pulsed neutron beam.
. In this paper detailed detector design is presented together with experimental results using the pulsed neutron beam.
Sanada, Yukihisa
Fukushima Inobeshon, Kosuto Koso, Hama Dori No Mirai O Hiraku Jitsuyoka Kaihatsu Purojekuto 2018-Nendoban, P. 35, 2019/05
no abstracts in English
Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Nishino, Sho; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko; Oishi, Tetsuya
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.134 - 138, 2019/01
At the severe nuclear accidents like the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, various radionuclides will be dispersed into the environment and raise the dose rate. The 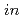 -
-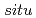 measurements of
measurements of  ray spectra and identifying radionuclides using the results are important for the radiological protection from both external and internal exposure. For this application a commercially available CdZnTe spectrometer (Kromek GR-1) was characterized at the calibration fields of FRS/JAEA. The angular dependence of the detection efficiency was studied and the efficiency was kept within 15 % degradation in
ray spectra and identifying radionuclides using the results are important for the radiological protection from both external and internal exposure. For this application a commercially available CdZnTe spectrometer (Kromek GR-1) was characterized at the calibration fields of FRS/JAEA. The angular dependence of the detection efficiency was studied and the efficiency was kept within 15 % degradation in  135 degree incident angle, which covers 85 % of all. The usable dose range was evaluated and the spectrometer could correctly measure the
135 degree incident angle, which covers 85 % of all. The usable dose range was evaluated and the spectrometer could correctly measure the  ray spectra below 200
ray spectra below 200  Gy/h.
Gy/h.
Kaburagi, Masaaki; Sato, Yuki; Yoshihara, Yuri*; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Torii, Tatsuo
Reactor Dosimetry; 16th International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry (ISRD-16) (ASTM STP 1608), p.405 - 414, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)